The ever-expanding clinical research landscape is driving up need for skilled CDM specialists. The Bureau of Labor Statistics predicts a 12% increase in job opportunities for medical and health services managers, which include CDM posts, between 2021 and 2031. Data analytics, technology, and increased access to the internet and healthcare have resulted in a paradigm shift in how clinical trials are conducted. Traditional clinical trials, which have long been used to gather data in support of medication, biological product, and medical device approval, have historically relied on traditional methods for data collecting, processing, and storage, often known as clinical data management (CDM). Paper-based data collection and transcription face significant challenges, which are constrained by factors such as the experience and skill of data handling specialists. Technological improvements have resulted in data management centralization, allowing data gathering and storage from multiple sites to be done securely and efficiently.
Importance of Clinical Data Management
Clinical Data Management (CDM) is crucial in ensuring that healthcare businesses meet regulatory standards and obligations. In the highly regulated healthcare industry, regulatory compliance is critical to the success of clinical trials and research studies. CDM is essential for assessing the safety and efficacy of therapies (such as medications and medical devices). Proper CDM guarantees that the data collected is comprehensive and can be utilized for statistical analysis, is formatted properly, and is transferable while accurately portraying the trial data obtained. Because data is so important to these organizations’ essential operations, it is critical that clinical data collected and processed be of high quality and managed with integrity. Understanding the CDM process can help understand both the value it provides and the effort required to maintain its effectiveness.
Why choose Clinical Data Management
Ensuring data integrity and quality is critical in medical research and patient care, with data accuracy and reliability serving as the cornerstone. Investing in good data management services is essential for maintaining these critical benchmarks. Clinical Data Management (CDM) is precisely developed to enhance this robustness by combining validation procedures and continual control monitoring. These verification mechanisms are critical to maintaining data integrity, acting as protective barriers against potential anomalies.
Career Growth Clinical Data Management
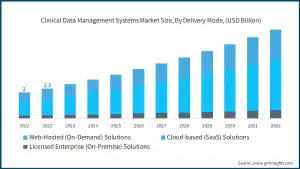 The career outlook for data scientists, including clinical data managers, is extremely favorable. The US Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) predicts that employment of data scientists will increase by 35% between 2022 and 2032, substantially faster than the average for all occupations. Clinical Data Management (CDM) is a fast expanding sector that provides excellent job opportunities for those with a life sciences background. With the increased demand for innovative medication development, there has never been a greater need for CDM professionals.
The career outlook for data scientists, including clinical data managers, is extremely favorable. The US Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) predicts that employment of data scientists will increase by 35% between 2022 and 2032, substantially faster than the average for all occupations. Clinical Data Management (CDM) is a fast expanding sector that provides excellent job opportunities for those with a life sciences background. With the increased demand for innovative medication development, there has never been a greater need for CDM professionals.
CURRICULUM
Introduction to Clinical Data Management (CDM)
- Role and Importance of CDM
- Data Management Life Cycle
- Regulatory and Ethical Standards
- Key Terminologies in CDM
- CDM Team Roles
Data Collection and CRF Design
- CRF Development
- Electronic Data Capture (EDC) Systems
- CRF Annotation and Completion Guidelines
- Source Data Verification (SDV)
- Data Standards and Coding
Data Cleaning and Validation
- Data Cleaning Techniques
- Query Management
- Data Validation Plan (DVP)
- Handling Missing Data
- Data Integrity and Security
Database Lock and Reporting
- Database Lock Procedures
- Statistical Analysis Readiness
- Generating Clinical Trial Reports
- Regulatory Submissions
- Archiving and Audit Trails







